PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF BASES
- Bitter taste: Almost all basic substances have a bitter taste.
- Action on litmus solution: Bases turn red litmus solution into blue.
- (Action on methyl orange: Bases turn methyl orange into yellow.
- Action on phenolphthalein: Bases turn phenolphthalein into pink.
- Conduction of electricity: Like acid, the aqueous solution of a base also conducts electricity.
Chemical Properties Of Bases
REACTION OF BASES WITH METALS:
Metals like zinc, tin and aluminum react with strong alkalies like NaOH (caustic soda), KOH (caustic potash) to evolve hydrogen gas.
Zn(s) + 2NaOH(aq) ![]() Na2ZnO2 (aq) + H2 (g)
Na2ZnO2 (aq) + H2 (g)
Sodium zincate
Sn(s) + 2NaOH(aq) ![]() Na2SnO2 (aq) + H2 (g)
Na2SnO2 (aq) + H2 (g)
Sodium stannite
2AI(s) + 2NaOH + 2H2O ![]() 2NaAIO2 (aq) + 3H2 (g)
2NaAIO2 (aq) + 3H2 (g)
Sodium meta aluminate
Experiment: Take 2-3 pieces of zinc granules in a test tube and add about 2-3 ml of conc. NaOH solution in to it and warm the contents.
Observation: There is evolution of ![]() gas which burns with a pop sound (on bringing a burning
candle near the mouth of tube).
gas which burns with a pop sound (on bringing a burning
candle near the mouth of tube).
The reaction involved is:
![]()
zinc sodium hydroxide sodium zincate hydrogen
(a metal) (conc.) (a salt) gas
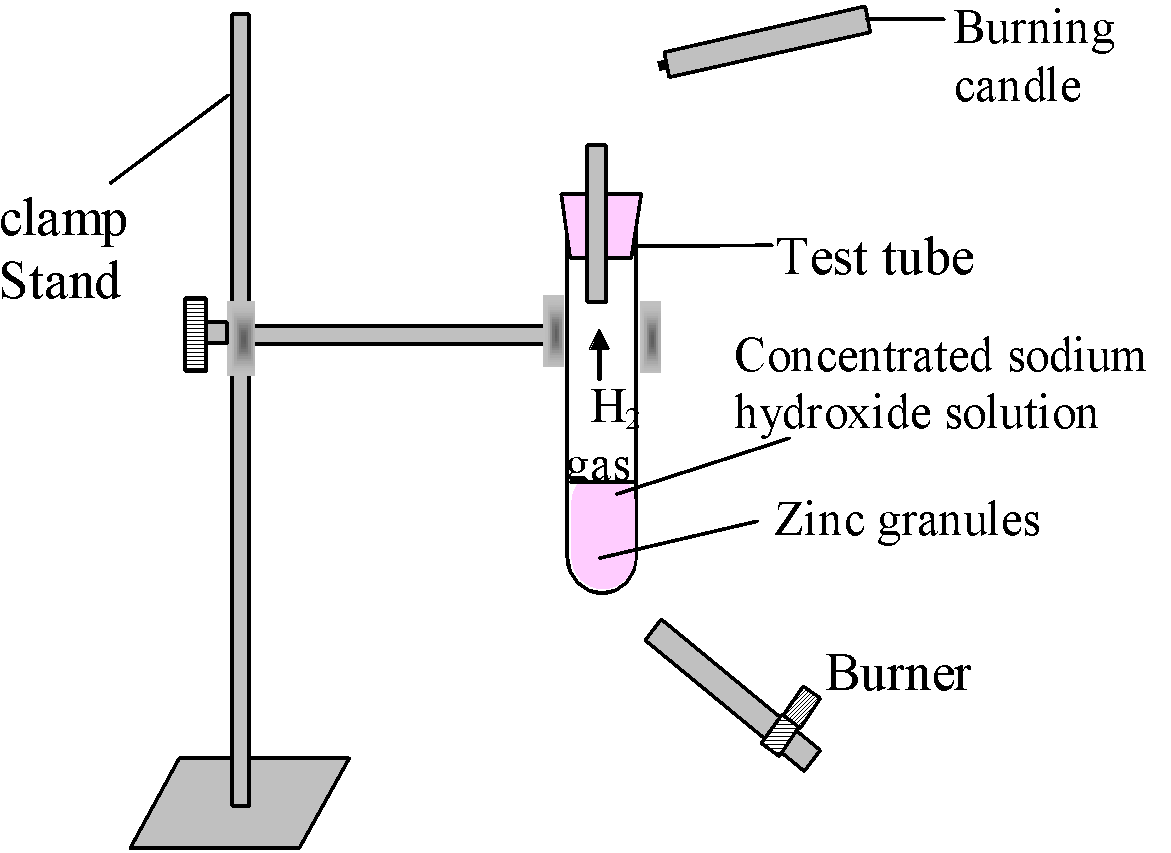
Figure-Study of the reaction of sodium hydroxide with Zn metal
|
|
All metals do not react with bases to form salts and hydrogen gas. |
REACTION OF BASES WITH ACIDS (NEUTRALIZATION REACTION)
When a base reacts with an acid then salt and water are formed
i.e. Base + Acid → Salt + Water
This reaction is called neutralization reaction, because when base and acid react with each other, they neutralize each other’s effect (i.e. acid destroys the basic property of a base and a base destroys the acidic property of an acid)
(i) ![]()
sodium hydroxide hydrochloric acid sodium chloride water
(base) (acid) (salt)
(ii) ![]()
sodium hydroxide sulphuric acid sodium sulphate water
(base) (acid) (salt)
Conclusion: Reaction of a base with an acid is a neutralization of an acid by base
REACTION OF BASE WITH NON-METAL OXIDE:
Bases react with non-metal oxide to form salt and water
i.e. Non-metal oxide + Base ![]() Salt + water
Salt + water
This reaction is similar to the neutralization reaction between acid and base to form salt and water. Thus, the reaction between bases and non-metal oxides is a kind of neutralization reaction and shows that non-metal oxides are acidic oxides.
⇒ Reaction of calcium hydroxide (lime water) with carbon dioxide.
Calcium hydroxide (lime water) is a base and carbon dioxide ![]() is a non-metal oxide, so when they react with each
other, salt and water are produced according to the reaction:
is a non-metal oxide, so when they react with each
other, salt and water are produced according to the reaction:
![]()
calcium hydroxide carbondioxide calcium water
(lime water) (non-metal oxide) carbonate
(base) (salt)
2NaOH(aq) + CO2 (g) ![]() Na3CO3 (aq) + H2O
Na3CO3 (aq) + H2O![]()
Ca(OH)2 (s) + SO2 (g) ![]() CaSO3 (aq) + H2O
CaSO3 (aq) + H2O![]()
Conclusion: Reactions of bases with non-metal oxides are neutralization reactions which show the acidic nature of non-metal oxide.
