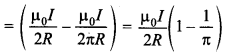Moving Charges and Magnetism Class 12 Physics MCQs Pdf
1. Two charged particles traverse identical helical paths in a completely opposite
sense in a uniform magnetic field B = B0\(\hat{k}\). [NCERT
Exemplar]
(a) They have equal z-components of momenta.
(b) They must have equal charges.
(c) They necessarily represent a particle- antiparticle pair.
(d) The charge to mass ratio satisfy:
\(\left(\frac{e}{m}\right)_{1}+\left(\frac{e}{m}\right)_{2}=0\)
Answer/Explanation
Answer: d
Explaination:
(d) Charged particles traverse identical helical paths in a completely opposite
sense in a uniform magnetic field B.
Therefore
\(\left(\frac{e}{m}\right)_{1}+\left(\frac{e}{m}\right)_{2}=0\)
2. Biot-Savart law indicates that the moving electrons (velocity v) produce a
magnetic field B such that [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) B ⊥ v.
(b) B || v.
(c) it obeys inverse cube law.
(d) it is along the line joining the electron and point of observation.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: a
Explaination:
(a) Magnetic field is given by
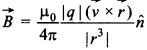
Where n is the direction of \(\vec{B}\) which is in the direction of cross
product of \(\vec{v}\) and \(\vec{r}\). Or we can say that \(\vec{B}\) ⊥ to both
\(\vec{v}\) and \(\vec{r}\).
3. A current carrying circular loop of radius R is placed in the x-y plane with
centre at the origin. Half of the loop with x > 0 is now bent so that it now lies
in the y – z plane. [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) The magnitude of magnetic moment now diminishes.
(b) The magnetic moment does not change.
(c) The magnitude of B at (0.0.z), z» R increases.
(d) The magnitude of B at (0, 0, z), z » R is unchanged.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: a
Explaination:
(a) Direction of magnetic moment (M= I A) of circular loop is perpendicular to
the loop as per right hand thumb rule.
The magnitudes of magnetic moment of each semicircular loop of radius R lie in
the x-y plane and y-z plane is M1 – M2= \(I
\frac{\pi R^{2}}{2}\) and the direction of magnetic moments are along
z-direction and ^-direction respectively. Their resultant
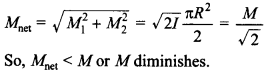
4. An electron is projected with uniform velocity along the axis of a current
carrying long solenoid. Which of the following is true? [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) The electron will be accelerated along the axis.
(b) The electron path will be circular about the axis.
(c) The electron will experience a force at 45° to the axis and hence execute a
helical path.
(d) The electron will continue to move with uniform velocity along the axis of the
solenoid.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: d
Explaination:
(d) F = -evB sin 180° = 0 (i.e 0= 0°or 180° in both cases F = 0). The electron
will continue to move with uniform velocity or will go undeflected along the
axis of the solenoid.
5. In a cyclotron, a charged particle [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) undergoes acceleration all the time.
(b) speeds up between the dees because of the magnetic field.
(c) speeds up in a dee.
(d) slows down within a dee and speeds up between dees.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: a
Explaination:
(a) It is based on the fact that the electric field accelerates a charged
particle and the perpendicular magnetic field keeps it revolving in circular
orbits of constant frequency.
6. A circular current loop of magnetic moment Mis in an arbitrary orientation in an
external magnetic field B. The work done to rotate the loop by 30° about an axis
perpendicular to its plane is [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) MB
(b) √3\(\frac{MB}{2}\)
(c) \(\frac{MB}{2}\)
(d) zero
Answer/Explanation
Answer: d
Explaination:
(d) The rotation of the loop by 30° about an axis perpendicular to its plane
makes no change in the angle made by axis of the loop with the direction of
magnetic field, therefore, the work done to rotate the loop is zero.
7. A rectangular loop carrying a current i is situated near a long straight wire such
that the wire is parallel to the one of the sides of the loop and is in the plane of
the loop. If a steady current I is established in wire as shown in figure, the loop
will
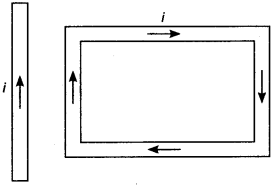
(a) rotate about an axis parallel to the wire.
(b) move away from the wire or towards right.
(c) move towards the wire.
(d) remain stationary.
Answer
Answer: c
8. A circular coil of radius 4 cm and of 20 turns carries a current of 3 amperes. It
is placed in a magnetic field of intensity of 0.5 weber/m². The magnetic dipole
moment of the coil is
(a) 0.15 ampere-m²
(b) 0.3 ampere-m²
(c) 0.45 ampere-m²
(d) 0.6 ampere-m²
Answer
Answer: b
9. A cubical region of space is filled with some uniform electric and magnetic
fields. An electron enters the cube across one of its faces with velocity v and a
positron enters via opposite face with velocity -v. At this instant,
(a) the electric forces on both the particles cause identical accelerations.
(b) the magnetic forces on both the particles cause equal accelerations.
(c) Only electron gains or looses energy.
(d) the motion of the centre of mass (CM) is determined by E alone.
Answer
Answer: b
10. Consider a wire carrying a steady current, I placed in a uniform magnetic field B
perpendicular to its length. Consider the charges inside the wire. It is known that
magnetic forces do not work. This implies that,
(a) motion of charges inside the conductor is unaffected by B, since they do not
absorb energy.
(b) Some charges inside the wire move to the surface as a result of B.
(c) if the wire moves under the influence of B, no work is done by the force.
(d) If the wire moves under the influence of B, no work is done by the electric
force on the ions, assumed fixed within the wire.
Answer
Answer: b
11. Two identical current carrying coaxial loops, carry current I in an opposite
sense. A simple amperian loop passes through both of them once. Calling the loop as
C,
(a) \(\oint_{C}\)B.dl = ± 2µ0I.
(b) the value of \(\oint_{C}\)B.dl is independent of sense of C. c
(c) there may be a point on C where, B and dl are parallel.
(d) B vanishes everywhere on C.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: b
Explaination:
(b) Ampere’s law gives another method to calculate the magnetic field due to a
given current distribution.
Applying the Ampere’s circuital law, we have
\(\oint_{C}\)B.dl = i0(I – I) = 0 (because current is in
opposite sense).
Also, there may be a point on C where B and dl are perpendicular and hence
\(\oint_{C}\)B.dl = 0
12. The strength of magnetic field at the centre of circular coil is
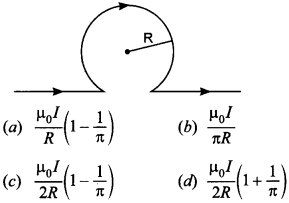
Answer/Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination:
(c) B = Field to circular portion
– Field due to straight portion