Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance Class 12 Physics MCQs Pdf
1. A positively charged particle is released from rest in an uniform electric field. The electric potential energy of the charge [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) remains a constant because the electric field is uniform.
(b) increases because the charge moves along the electric field.
(c) decreases because the charge moves along the electric field.
(d) decreases because the charge moves opposite to the electric field.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination:
(c) The positively charged particle experiences electrostatic force along the direction of electric field, hence moves in the direction of electric field. Electric potential decreases in the direction of electric field. Thus, positive work is done by the electric field on the charge.
We = -ΔU = -qΔV=q(Vin – Vf)
Hence electrostatic potential energy of the positive charge decreases.
2. Figures show some equipotential lines distributed in space. A charged object is moved from point A to point B. [NCERT Exemplar]
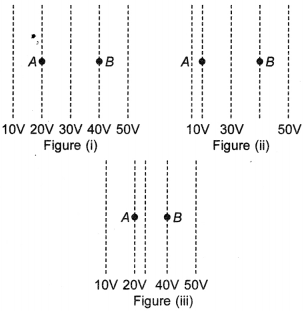
(a) The work done in Fig. (i) is the greatest.
(b) The work done in Fig. (ii) is least.
(c) The work done is the same in Fig. (i), Fig.(ii) and Fig. (iii).
(d) The work done in Fig. (iii) is greater than Fig. (ii) but equal to that in Fig. (i).
Answer/Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination:
(c) The work done by the electric field on the charge will be negative.
Welectrical = -ΔU = – qΔV— q( Vinitial – Vfinal) Here initial and final potentials are same in all three cases and the same charge is moved, so work done is same in all three cases.
3. Equipotentials at a great distance from a collection of charges whose total sum is not zero are approximately [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) spheres
(b) planes
(c) paraboloids
(d) ellipsoids
Answer/Explanation
Answer: a
Explaination:
(a) The collection of charges at great distance is considered as a single point charge. The equipotential surfaces due to a point charge are spherical.
4. Two small spheres each carrying a charge q are placed r metre apart. If one of the spheres is taken around the other one in a circular path of radius r, the work done will be equal to
(a) force between them × r
(b) force between them × 2πr
(c) force between them/2πr
(d) zero
Answer/Explanation
Answer: d
Explaination: (d) The force is perpendicular to the displacement.
5. The electric potential V at any point O (x, y, z all in metres) in space is given by V = 4x² volt. The electric field at the point (1 m, 0, 2 m) in volt/metre is
(a) 8 along negative x-axis
(b) 8 along positive x-axis
(c) 16 along negative x-axis
(d) 16 along positive z-axis
Answer/Explanation
Answer: a
Explaination: (a) The electric field E = \(\frac{-dV}{dx}\) = -8x V/m
6. If a unit positive charge is taken from one point to another over an equipotential surface, then
(a) work is done on the charge.
(b) work is done by the charge.
(c) work done is constant.
(d) no work is done.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: d
Explaination:
(d) On the equipotential surface, electric field is normal to the charged surface (where potential exists) so that no work will be done.
7. A hollow metal sphere of radius 5 cm is charged so that the potential on its surface is 10 V. The potential at the centre of the sphere is
(a) 0 V
(b) 10 V
(c) Same as at point 5 cm away from the surface
(d) Same as at point 25 cm away from the surface
Answer/Explanation
Answer: b
Explaination: (b) Since potential inside the hollow sphere is same as that on the surface.
8. The electrostatic force between the metal plates of an isolated parallel plate capacitor C having a charge Q and area A, is
(a) proportional to the square root of the distance between the plates.
(b) linearly proportional to the distance between the plates.
(c) independent of the distance between the plates.
(d) inversely proportional to the distance between the plates.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination:
(c) For isolated capacitor Q = Constant,
force between plate = \(\frac{Q^{2}}{2 A \varepsilon_{0}}\).
9. A capacitor is charged by a battery. The battery is removed and another identical uncharged capacitor is connected in parallel. The total electrostatic energy of resulting system
(a) increases by a factor of 4.
(b) decreases by a factor of 2.
(c) remains the same.
(d) increases by a factor of 2.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: b
Explaination: (b) Using, Vc = \(\frac{V}{2}\), U = \(\frac{1}{2}\)CV².
10. A conductor with a positive charge
(a) is always at +ve potential.
(b) is always at zero potential.
(c) is always at negative potential.
(d) may be at +ve, zero or -ve potential.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: d
Explaination:
(d) May be at positive, zero or negative potential, it is according to the way one defines the zero potential.