Current Electricity Class 12 Physics MCQs Pdf
1. Consider a current carrying wire current I in the shape of a circle. Note that as
the current progresses along the wire, the direction of j (current density) changes
in an exact manner, while die current/remain unaffected. The agent that is
essentially responsible for is [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) source of emf.
(b) electric field produced by charges accumulated on the surface of wire.
(c) the charges just behind a given segment of wire which push them just the right
way by repulsion.
(d) the charges ahead.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: b
Explaination:
(b) Current density j changes due to electric field produced by charges
accumulated on the surface of wire.
2. Two batteries of ε1 and ε2 (ε2 >
ε1) and internal resistance r1 and r2 respectively
are connected in parallel as shown in figure. [NCERT Exemplar]
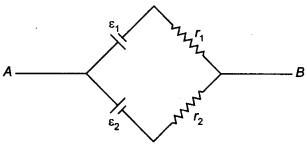
(a ) The equivalent emf εeq of the two cells is between ε1 and
ε2 i.e. ε1 < εeq < ε2.
(b) The equivalent emf εeq is smaller than ε1.
(c) The eeq is given by εeq= ε1 + ε2 always.
(d) zeq is independent of internal resistances r1 and r2.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: a
Explaination:
(a) The equivalent emf of this combination is given by
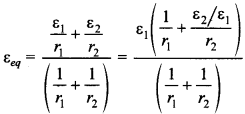
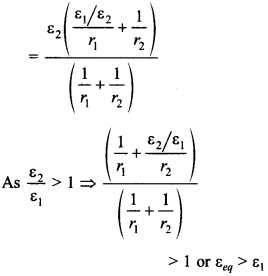

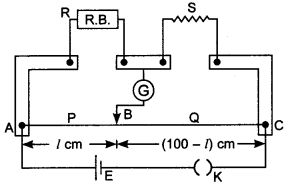
3. A resistance R is to be measured using a meter bridge. Student chooses the
standard resistance S to be 100 Ω He finds the null point at l1 = 2.9 cm.
He is told to attempt to improve the accuracy. Which of the following is a useful
way? [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) He should measure l1 more accurately.
(b) He should change Sto 1000 Ω and repeat the experiment.
(c) He should change S to 3 Ω and repeat the experiment.
(d) He should give up hope of a more accurate measurement with a meter bridge.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination:
(c) The bridge is said to be balanced if the ratio of the resistances in same
branch is equal
![]()
Since here, R : S = 2.9 : 97.1, then the value of S is nearly 33 times to that
of R. In order to make this ratio 1 : 1, it is necessary to reduce the value of
S nearly \(\frac{1}{33}\) times i.e., nearly 3 Ω.
4. Two cells of emf’s approximately 5 V and 10 V are to be accurately compared using
a potentiometer of length 400 cm. [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) The battery that runs the potentiometer should have voltage of 8 V.
(b) The battery of potentiometer can have a voltage of 15 V and R adjusted so that
the potential drop across the wire slightly exceeds 10 V.
(c) The first portion of 50 cm of wire itself should have a potential drop of 10
V.
(d) Potentiometer is usually used for comparing resistances and not voltages.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: b
Explaination:
(b) The potential drop along the wires of potentiometer should be greater than
emfs of cells. Here, values of emfs of two cells are given as 5 V and 10 V,
therefore, the potential drop along the potentiometer wire must be more than 10
V.
5. Consider a simple circuit shown in figure stands for a variable resistance
R’. R’ can vary from R0 to infinity, r is internal resistance
of the battery (r << R << R0). [NCERT Exemplar]
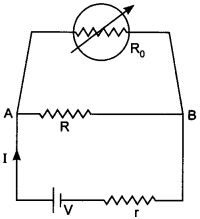
(a) Potential drop across AB is not constant as R0 is varied.
(b Current through R0 is nearly a constant as R0 is varied.
(c) Current I depends sensitively on R0.
(d) \(I \geq \frac{V}{r+R}\) always.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: d
Explaination:
(d) In parallel grouping of resistance, same potential difference appeared
across each resistance but current distributed in reverse ratio of their
resistance,
i.e i ∝ \(\frac{1}{R}\)
P.d across AB and r = v, equivalent resistance of parallel combination R’
< R, therefore current
\(I \leq \frac{V}{R+r}\)
6. In a meter bridge, the point D is a neutral point (figure). [NCERT Exemplar]
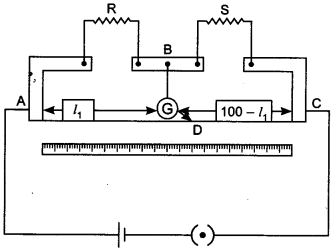
(a) The meter bridge can have other neutral point for this set of resistances.
(b) When the jockey contacts a point on meter wire left of D, current flows to B
from the wire.
(c) When the jockey contacts a point on the meter wire to the right of D, current
flows from B to the wire through galvanometer.
(d) When R is increased, the neutral point shifts to left.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination:
(c) If in balanced position of bridge AB = l,
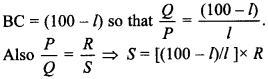
When there is no deflection in galvanometer there is no current across the
galvanometer, then points B and D are at same potential. That point at which
galvanometer shows no deflection is called null point, When the jockey contacts
a point on the meter wire to the right of D, the potential drop across AD is
more than potential drop across AB, which brings the potential of point D less
than that of B, hence current flows from B to D in the galvanometer wire.
7. Which of the following is wrong? Resistivity of a conductor is
(a) independent of temperature.
(b) inversely proportional to temperature.
(c) independent of dimensions of conductor.
(d) less than resistivity of a semiconductor.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: a
Explaination:
(a) Resistivity is property of material and inversely proportional to
temperature for conductor, \(\rho=\frac{m}{n e^{2} \tau}\).
8. Drift velocity vd varies with the intensity of electric field as per the
relation
(a) vd ∝ E
(b) vd ∝ \(\frac{1}{E}\)
(c) vd = constant
(d) vd ∝ E²
Answer/Explanation
Answer: a
Explaination:
(a) Drift velocity vd = \(\frac{e E}{m} \tau\), i.e. vd ∝
E
9. For measurement of potential difference, a potentiometer is preferred over
voltmeter because
(a) potentiometer is more sensitive than voltmeter.
(b) the resistance of potentiometer is less than voltmeter.
(c) potentiometer is cheaper than voltmeter.
(d) potentiometer does not take current from the circuit.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: (d) Potentiometer works on null deflection method.
10. For a cell, the graph between the potential difference (V) across the terminals
of the cell and the current (I) drawn from the cell is shown in the figure.
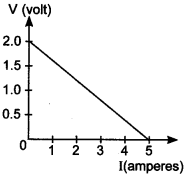
The e.m.f. and the internal resistance of the cell are
(a) 2V, 0.5 Ω
(b) 2V, 0.4 Ω
(c) > 2V, 0.5 Ω
(d) > 2V, 0.4 Ω
Answer/Explanation
Answer: b
Explaination:
(b) E.m.f. is the value of voltage, when no current is drawn from the circuit so
E= 2 V.
Also r = slope = \(\frac{2}{5}\) = 0.4 Ω