Electric Charges and Fields Class 12 Physics MCQs Pdf
25. The force per unit charge is known as
(a) electric flux
(b) electric field
(c) electric potential
(d) electric current
Answer
Answer: b
26. Electric field lines provide information about
(a) field strength
(b) direction
(c) nature of charge
(d) all of these
Answer
Answer: d
27. Which of the following figures represent the electric field lines due to a single
negative charge?
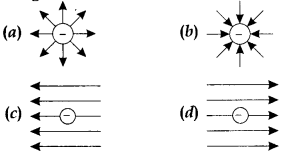
Answer
Answer: b
28. The SI unit of electric flux is
(a) N C-1 m-2
(b) N C m-2
(c) N C-2 m2
(d) N C-1 m2
Answer
Answer: d
29. The unit of electric dipole moment is
(a) newton
(b) coulomb
(c) farad
(d) debye
Answer
Answer: d
30. Consider a region inside which, there are various types of charges but the total
charge is zero. At points outside the region
(a) the electric field is necessarily zero.
(b) the electric field is due to the dipole moment of the charge distribution
only.
(c) the dominant electric field is inversely pro-portional to r3, for large r
(distance from ori-gin).
(d) the work done to move a charged particle along a closed path, away from the
region will not be zero.
Answer
Answer: c
31. The surface considered for Gauss’s law is called
(a) Closed surface
(b) Spherical surface
(c) Gaussian surface
(d) Plane surface
Answer
Answer: c
32. The total flux through the faces of the cube with side of length a if a charge q
is placed at corner A of the cube is
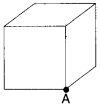

Answer
Answer: a
33. Which of the following statements is not true about Gauss’s law?
(a) Gauss’s law is true for any closed surface.
(b) The term q on the right side side of Gauss’s law includes the sum of all
charges enclosed by the surface.
(c) Gauss’s law is not much useful in calculating electrostatic field when the
system has some symmetry.
(d) Gauss’s law is based on the inverse square dependence on distance
contained in the coulomb’s law
Answer
Answer: c
34. Four charges are arranged at the comers of a square ABCD, as shown. The force on
the charge kept at the centre O is
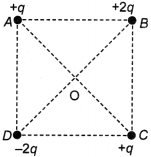
(a) zero
(b) along the diagonal AC
(c) along the diagonal BD
(d) perpendicular to side AB
Answer/Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination:
(c) Place a unit positive charge at O. Resultant force due to the charges placed
at A and C is zero and resultant charge due to B and D is towards D along the
diagonal BD.
35. One end of a copper wire is connected to a neutral pith ball and other end to a negatively charged plastic rod. What will be the charge acquired by a pith ball? [Chennai 2019]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Negative charge.
36. Distinguish between an insulator (dielectric) and a conductor.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
Dielectrics do not have free electrons, while conductors have free electrons.
When some charge is transferred to a conductor, it readily gets distributed over
the entire surface of the conductor, but on insulators, the charge stays at the
same place.