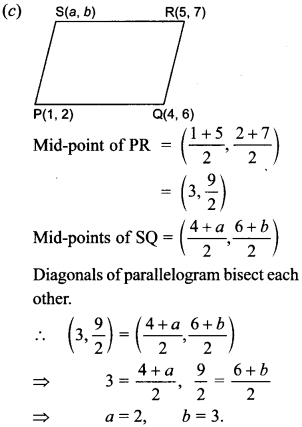
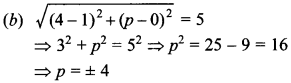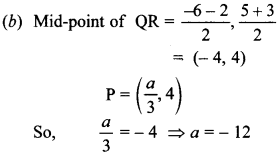In the current scenerio Practicing NCERT Maths MCQ for Class 10 CBSE with Answers Pdf is one of the best ways to prepare for the CBSE Class 10 board exam. There is no substitute for consistent practice whether one wants to understand a concept thoroughly or one wants to score better. The given questions will help to understand the chapter at minute levels. Also the new pattern of CBSE Board will more emphasis on the Multiple choice questions.So there is need also. We will came with more and more such types of problems.
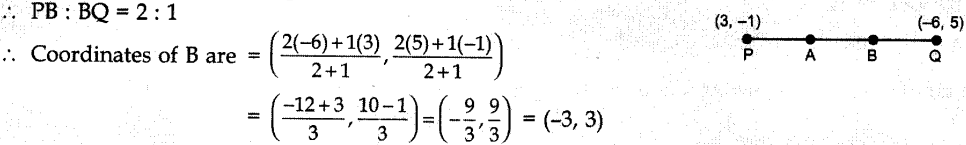
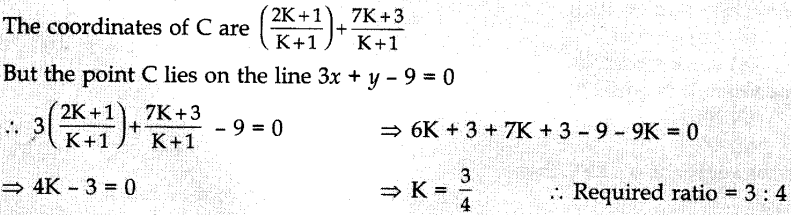
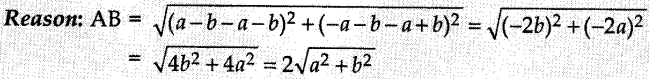
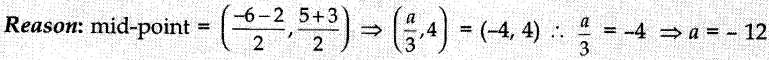
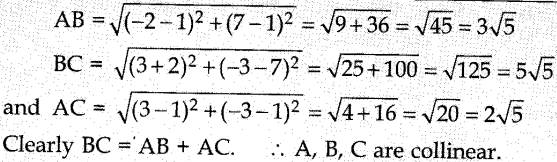
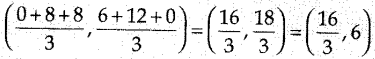
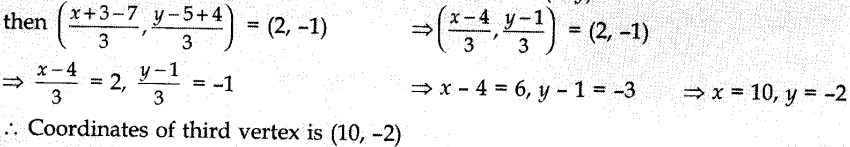
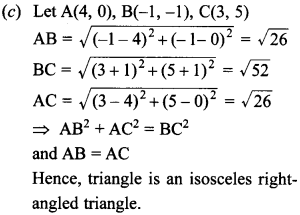
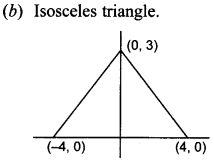
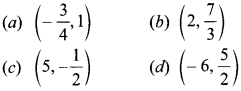
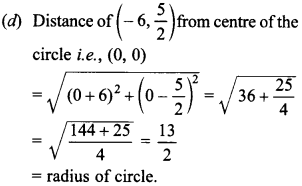
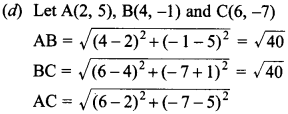
 `
`